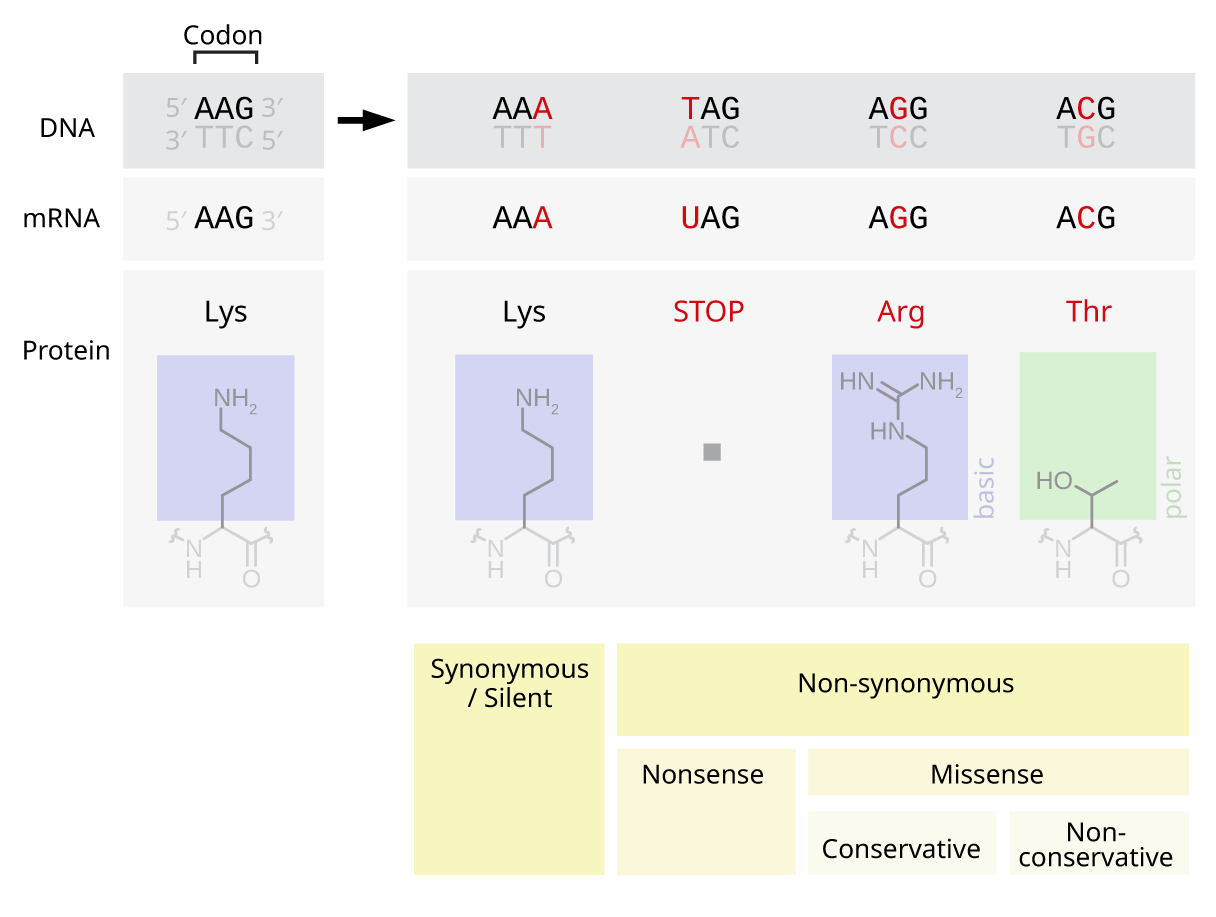
All mutations can have an effect on a gene, but some specific mutations can make a big difference in the DNA sequence. Deletion or insertion (both frameshift mutations) at the beginning of a sequence seem to affect the whole sequence the most because it changes all of the amino acids after it. Also, it can even cause the translating not to start at all. The mutation that has the least effect was substitution because it only changes one amino acid out of the whole chain.
I chose deletion for my own mutation because I thought that it would cause the most change (damage) to the chain of amino acids. It changed many of the amino acids after it. By placing this mutation at the beginning of the sequence, it changed all the amino acids as a result. Because of this change in all of the amino acids, the protein would probably not do what it is supposed to do, and it wouldn't function correctly.
Progeria causes accelerated aging. It is caused by a mutation in the LMNA gene, a protein which provides support to the nucleus of a cell. Most people who have progeria die by the age of 13, due to age-related health problems. Progeria interests scientists who are trying to connect certain genes with aging.
(LMNA Gene)



No comments:
Post a Comment